Propose a fragmentation to account for each numbered peak in the mass spectrum of n-butyl isopropyl ether.
<IMAGE>
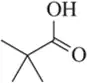
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: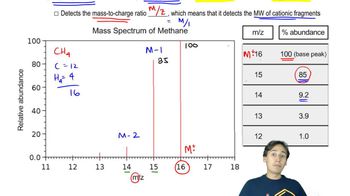

 4:28m
4:28mMaster Ionization Potentials with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning