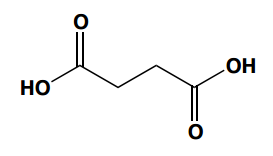
In organic chemistry, diacids are compounds that contain two carboxylic acid groups (-COOH) within the same molecular structure. Understanding the simplest diacids is essential, as they often play significant roles in various chemical reactions and applications. The first three simplest diacids to be familiar with are oxalic acid, malonic acid, and succinic acid.
Oxalic acid, with the formula C_2H_2O_4, is the simplest diacid and is known for its strong acidity. Malonic acid, represented as C_3H_4O_4, is particularly important in synthetic organic chemistry and is frequently encountered in various reactions. Succinic acid, with the formula C_4H_6O_4, is also relevant but to a lesser extent than malonic acid.
To help remember these diacids, you can use the mnemonic "Oh my science," which corresponds to the first letters of each acid: O for oxalic, M for malonic, and S for succinic. This catchy phrase can aid in recalling these important compounds throughout your studies.