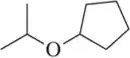
The base peak in Figure 14.51 has m/z 45. Suggest a molecular formula and a structure for this fragment.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: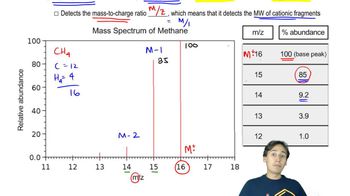

 4:28m
4:28mMaster Ionization Potentials with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning