In the study of chemical reactions, it is essential to recognize the four major types of reactions that frequently occur. Understanding these categories will help you identify the nature of a reaction based on its general features, even if you do not grasp all the underlying mechanisms yet. This foundational knowledge is crucial, as it may be tested in multiple-choice questions on your exams.
The four primary types of reactions include:
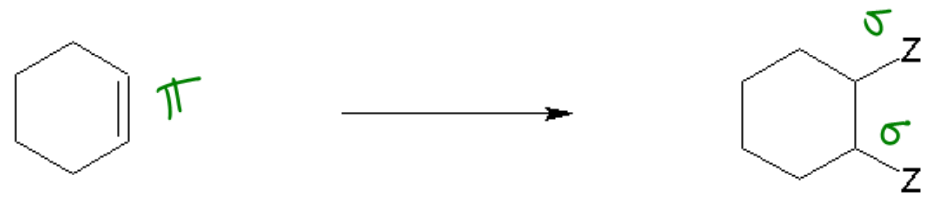
1. Synthesis Reactions: In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a single product. This can be represented by the general equation:
A + B → AB
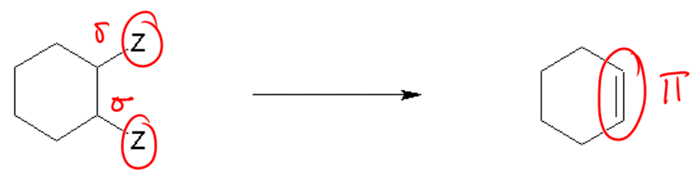
2. Decomposition Reactions: A decomposition reaction occurs when a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler products. The general form is:
AB → A + B
3. Single Replacement Reactions: In a single replacement reaction, one element replaces another in a compound. This can be expressed as:
A + BC → AC + B
4. Double Replacement Reactions: A double replacement reaction involves the exchange of ions between two compounds, resulting in the formation of two new compounds. The general equation is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
By familiarizing yourself with these reaction types, you will be better equipped to analyze and categorize reactions in organic chemistry, enhancing your overall understanding and performance in the subject.