The mass spectra of 1-methoxybutane, 2-methoxybutane, and 2-methoxy-2-methylpropane are shown below. Match each compound with its spectrum.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: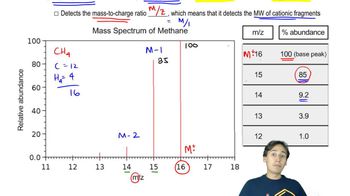
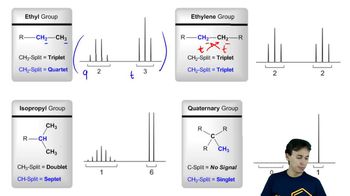

 4:28m
4:28mMaster Ionization Potentials with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning