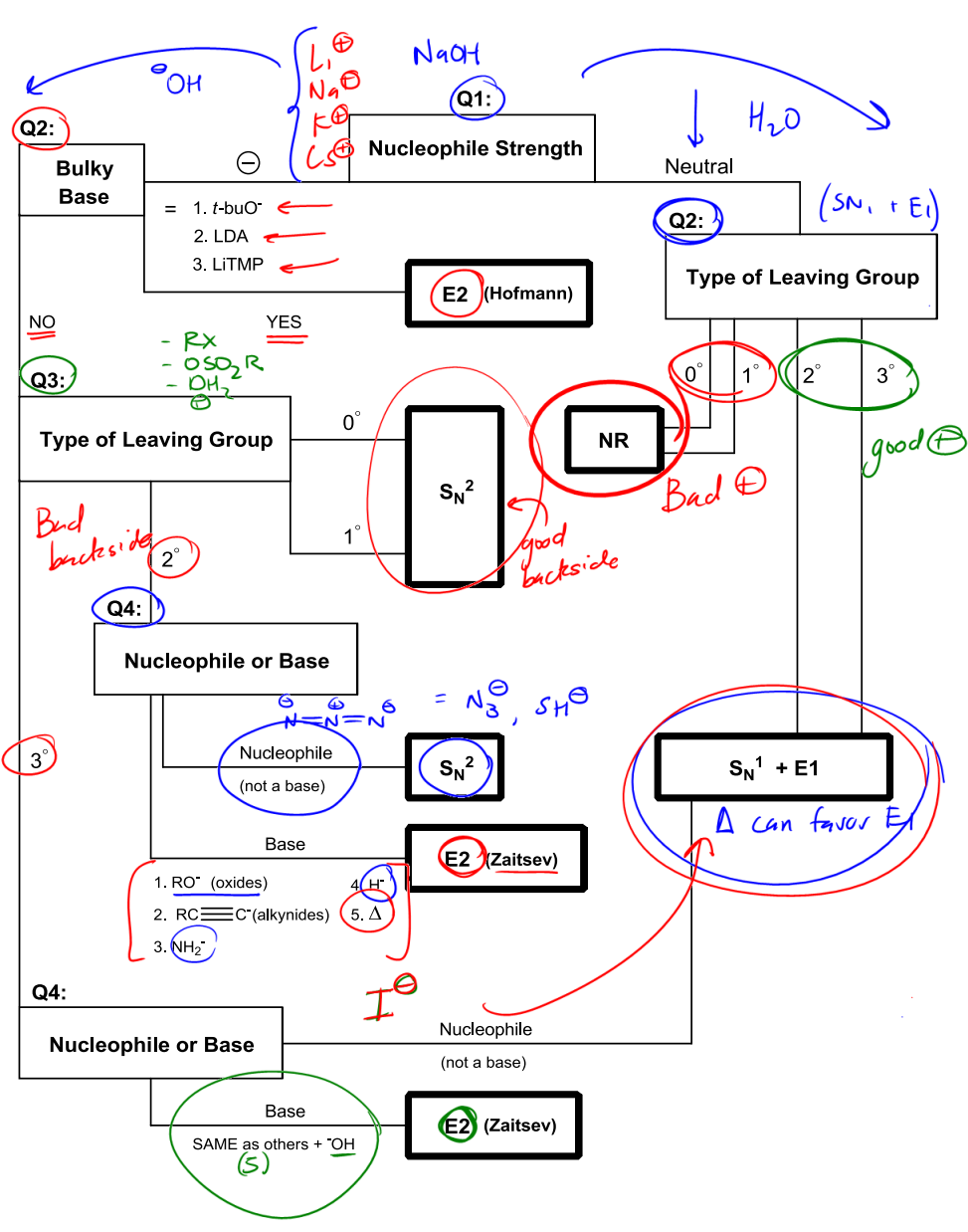
Understanding the mechanisms of nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions, specifically SN1, SN2, E1, and E2, can be challenging due to the overlapping conditions that favor each pathway. To simplify this process, a systematic approach can be employed using a flowchart, often referred to as the "Big Daddy Flowchart." This tool is designed to guide students through a series of questions that help determine the appropriate mechanism based on the characteristics of the nucleophile involved.
The first and most crucial question to consider is the nature of the nucleophile: is it strong or weak? This determination is typically made by assessing whether the nucleophile carries a negative charge or is neutral. A negatively charged nucleophile indicates a pathway towards the left side of the flowchart, while a neutral nucleophile directs the inquiry to the right side. It is important to note that positively charged species do not act as nucleophiles; instead, they are classified as electrophiles.
As you navigate through the flowchart, each question leads you closer to identifying the correct mechanism. For instance, if the nucleophile is strong and negatively charged, you may be led towards an SN2 or E2 mechanism, depending on other factors such as substrate structure and sterics. Conversely, if the nucleophile is weak or neutral, you might explore SN1 or E1 pathways. This structured questioning not only clarifies the decision-making process but also reinforces the underlying principles of nucleophilicity and electrophilicity.
By utilizing this flowchart, students can effectively visualize and categorize the mechanisms, making it easier to tackle complex reaction scenarios. This method has proven beneficial for many learners, including those preparing for standardized tests like the MCAT, as it provides a clear framework for understanding and applying these fundamental concepts in organic chemistry.