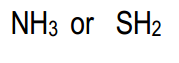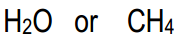Understanding acid-base equilibrium is crucial in chemistry, especially when determining the strength of acids without relying on pKa values. When pKa information is unavailable or when comparing acids with similar pKa values, we can utilize five key factors that influence acidity. These factors help us assess which acid is stronger by examining the stability of their conjugate bases.
The stability of the conjugate base is a significant indicator of an acid's willingness to donate a proton. A more stable conjugate base indicates that the acid is more likely to dissociate and release a proton. Conversely, if the conjugate base is unstable, the acid will be less inclined to lose its proton. This relationship is essential for understanding acid strength and the dynamics of acid-base reactions.
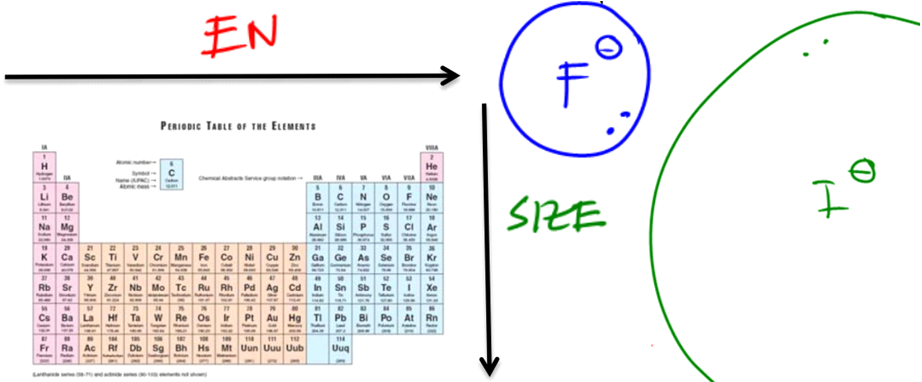
To analyze acidity without pKa values, we focus on the following five factors that affect the stability of the conjugate base:
- Electronegativity: The more electronegative an atom is, the better it can stabilize a negative charge. Thus, if the conjugate base has a highly electronegative atom, it will be more stable.
- Size of the Atom: Larger atoms can better accommodate negative charges due to their ability to spread out the charge over a larger volume. Therefore, conjugate bases derived from larger atoms tend to be more stable.
- Resonance: If the negative charge on the conjugate base can be delocalized through resonance structures, the stability of the conjugate base increases, making the corresponding acid stronger.
- Inductive Effect: Electron-withdrawing groups can stabilize a negative charge on the conjugate base through the inductive effect, enhancing the acid's strength.
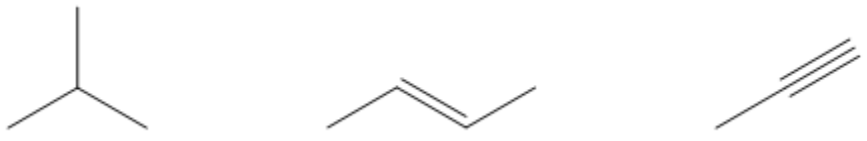
- Hybridization: The type of hybridization of the atom bearing the negative charge affects stability. For example, sp-hybridized carbons hold a negative charge more stably than sp2 or sp3 hybridized carbons.
By applying these factors, we can effectively determine the relative acidity of compounds even in the absence of pKa values. This approach not only deepens our understanding of acid-base chemistry but also enhances our ability to predict the behavior of various chemical species in reactions.