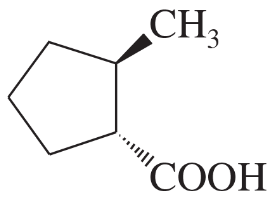
Draw the structures of the following compounds.
(f) salicylic acid
(g) zinc undecanoate (athlete's-foot powder)
(h) sodium benzoate (a food preservative)
(i) sodium fluoroacetate (Compound 1080, a controversial coyote poison)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:20m
4:20mMaster Carboxylic Acids Nomenclature with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning