All of the following names are incorrect or incomplete. In each case, draw the structure (or a possible structure) and name it correctly.
a. 3-ethyl-4-methylpentane
b. 2-ethyl-3-methylpentane
c. 3-dimethylhexane
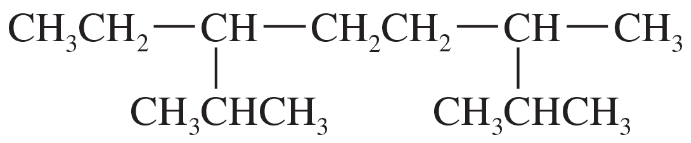
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning