Name the following alkanes and haloalkanes. When two or more substituents are present, list them in alphabetical order.
(a)
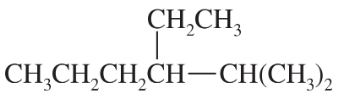
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 3:43m
3:43mMaster The different parts of an IUPAC name with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning