For each of the following compounds,
1. give the IUPAC name.
2. give the common name (if possible).
3. classify the compound as a methyl, primary, secondary, or tertiary halide.
(a) (CH3)2CHCH2Cl
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
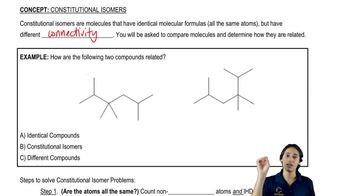
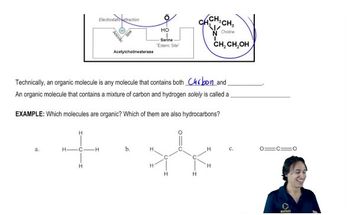
Verified video answer for a similar problem: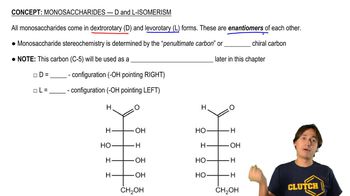

 1:52m
1:52mMaster How to name alkyl halides with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning