Identify the following alkynes as terminal (T), internal/symmetrical (IS), or internal/unsymmetrical (IU).
(c)
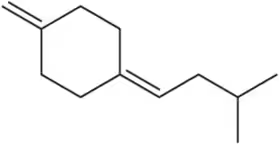
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 1:55m
1:55mMaster How to name alkenes and alkynes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning