Draw structural formulas of at least two alkynes of each molecular formula.
1. C6H10
2. C8H12
3. C7H8
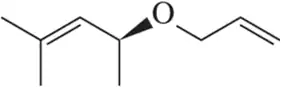
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: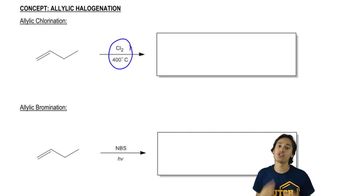
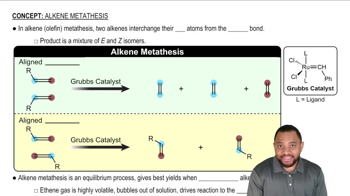

 1:55m
1:55mMaster How to name alkenes and alkynes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning