Textbook Question
Name the following alkenes, being sure to specify whether they are cis or trans.
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: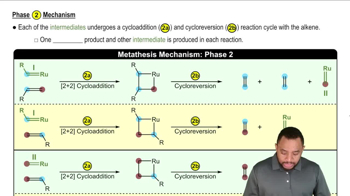
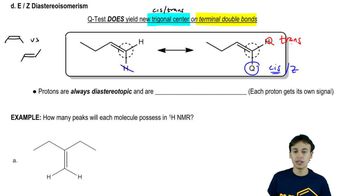


 4:28m
4:28mMaster How to name different types of double bonds or rings with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning