Textbook Question
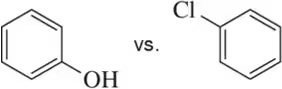
Ansaid and Motrin belong to the group of drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Both are only slightly soluble in water, but one is a little more soluble than the other. Which of the drugs has the greater solubility in water?