Textbook Question
Keto–enol tautomerism is a reaction we discuss in detail in Chapter 19. Estimate the equilibrium constant of this reaction (BDE for C―C π bond = 65 kcal/mol ; for C―O π bond = 85 kcal/mol).
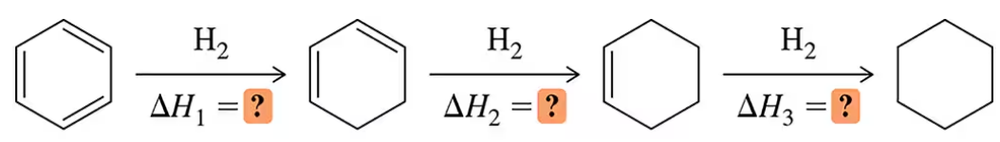
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:09m
4:09mMaster How to calculate enthalpy using bond dissociation energies. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning