For the following values of ∆H° , ∆S°, and T, tell whether the process would be favored.
(d) ∆H° = -8.3 kcal/mol ; ∆S° = -12 cal/mol•K ; T = 298 K
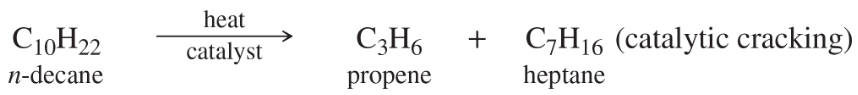
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:46m
2:46mMaster Explaining what entropy is. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning