Suggest a method for synthesizing the following alkynes using an alkyne and an alkyl halide. [There are two correct answers for each product.]
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: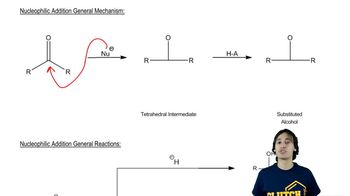



 3:19m
3:19mMaster Sodium Alkynide Alkylation with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning