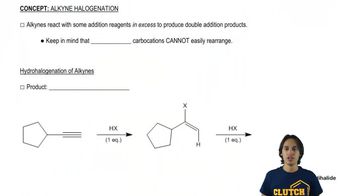
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared using the given starting material, any needed inorganic reagents, and any organic compound that has no more than four carbons:
b.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: