You drew the Lewis structures of the following compounds and ion in Assessment 2.32. Predict their shapes around the central atom based on the Lewis structure.
(c) HCO2H
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: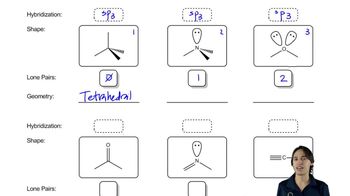


 7:44m
7:44mMaster Molecular Geometry Explained. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning