Describe the orbitals used in bonding and the bond angles in the following compounds:
a. CH3O-
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: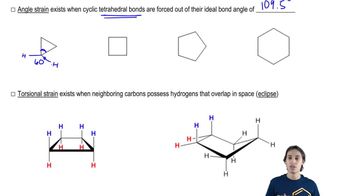
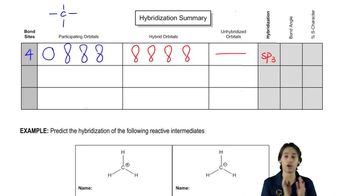
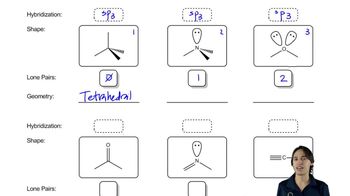

 7:44m
7:44mMaster Molecular Geometry Explained. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning