For each of the following pairs of reactions, indicate which one has the more favorable equilibrium constant (that is, which one most favors products):
1.
2.
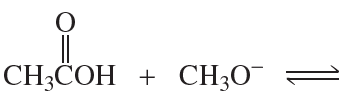
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 5:11m
5:11mMaster The 3 steps for determining the direction of acid and base equilibrium. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning