Which of the following bases can remove a proton from acetic acid in a reaction that favors products?
HO− CH3NH2 HC≡C− CH3OH H2O Cl−
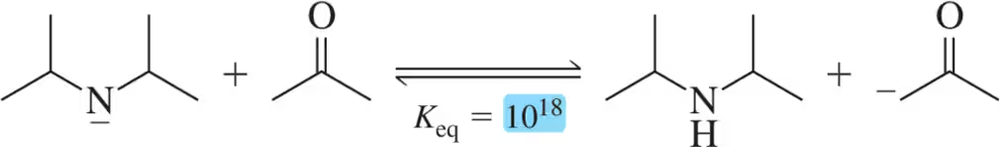
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: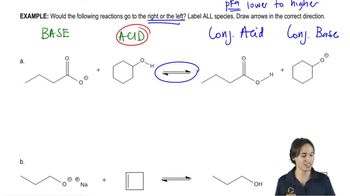

 5:11m
5:11mMaster The 3 steps for determining the direction of acid and base equilibrium. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning