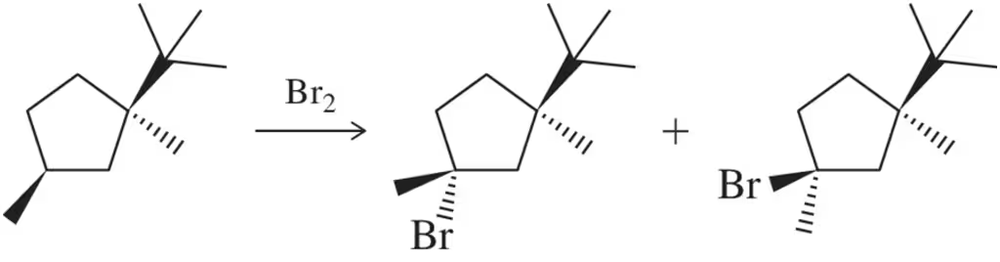
The radical fluorination of 2-methyl propane resulted in a 14:86 ratio of products.
(b) From the relative reactivity, calculate the difference in energy between the transition states of the first propagation steps leading to a 1° and 3° radical.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:05m
2:05mMaster The one reaction that alkanes will actually undergo. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning