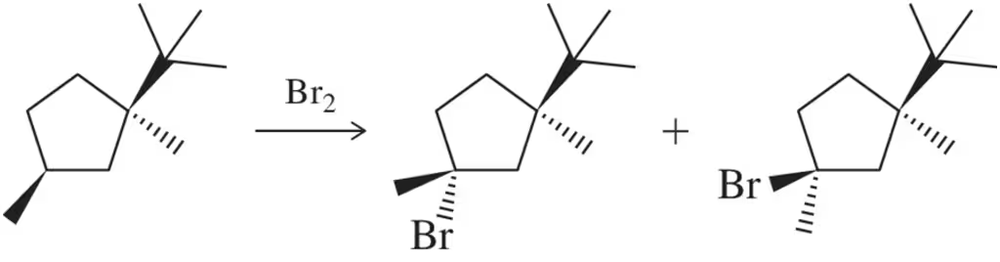
Show how free-radical halogenation might be used to synthesize the following compounds. In each case, explain why we expect to get a single major product.
(a) 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane (neopentyl chloride)
(b) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:



 2:05m
2:05mMaster The one reaction that alkanes will actually undergo. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning