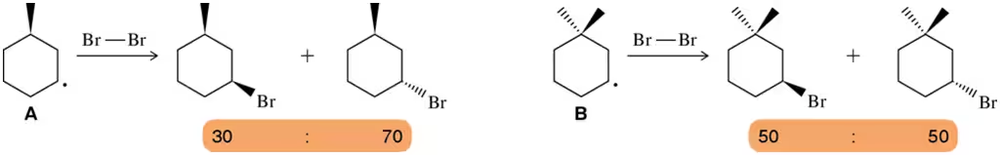
Predict the major monohalogenation product(s) of the following reactions. Indicate whether you think the reaction will be selective and justify your position.
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:05m
2:05mMaster The one reaction that alkanes will actually undergo. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning