Calculate the dihedral angle (θ) for the conformations shown.
(c)
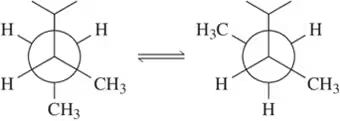
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: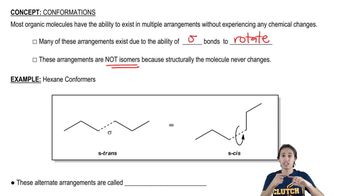
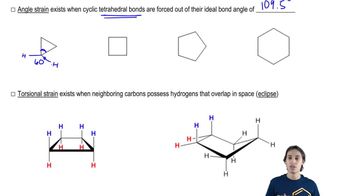


 3:11m
3:11mMaster How sigma bond rotation is visualized with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning