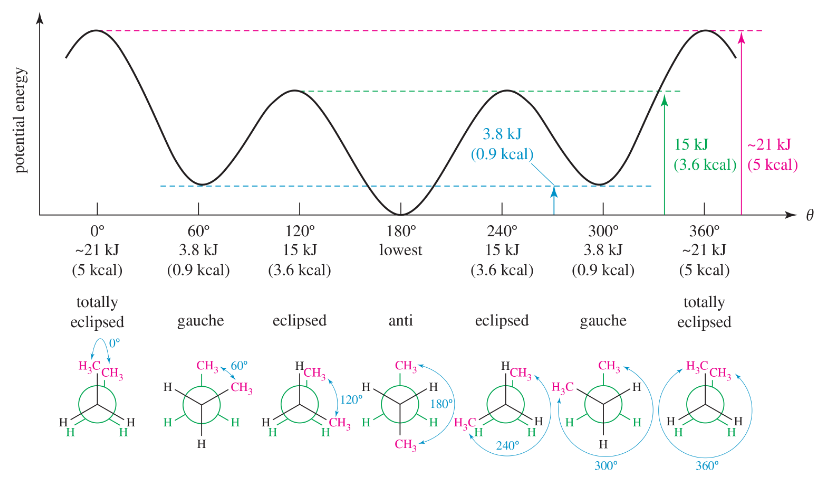
For each of the pairs in Assessment 3.29, which conformation would you expect to be more prominent at equilibrium?
(a)
(b)
(c)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: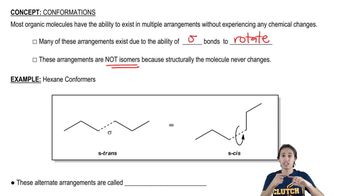
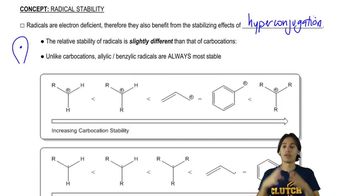
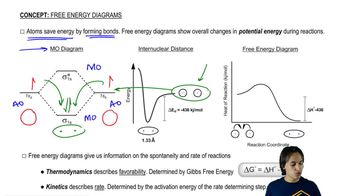

 3:11m
3:11mMaster How sigma bond rotation is visualized with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning