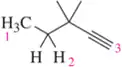
Predict the splitting patterns for the signals given by the compounds in Problem 4.
j.
 Verified step by step guidance
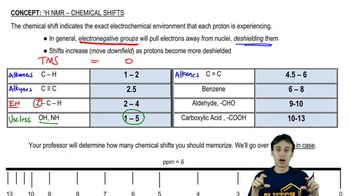
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: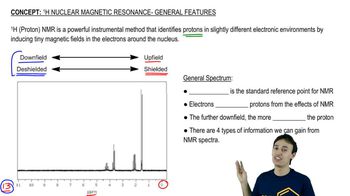


 12:21m
12:21mMaster Splitting without J-values with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning