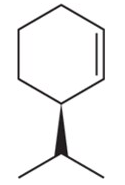
Define the relationship between each set of two molecules as chain isomers, positional isomers, functional group isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, conformational isomers, or identical
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
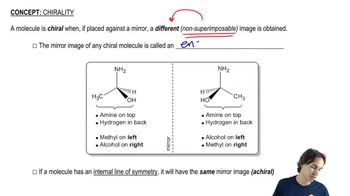


 3:51m
3:51mMaster Determining when molecules are different. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning