Give the relationship between the following pairs of structures. The possible relationships are:
same compound
constitutional isomers (structural isomers)
cis-trans isomers
not isomers (different molecular formula)
(a)
(b)
(c)
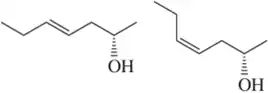
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: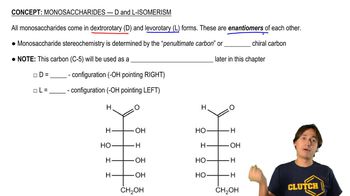
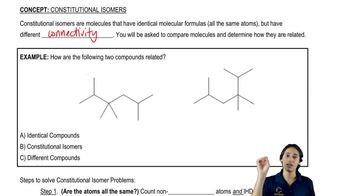

 3:51m
3:51mMaster Determining when molecules are different. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning