Label each hydrogen atom in the following compounds as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°).
(c) (CH3)2CHCH(CH3)CH2CH3
(d)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: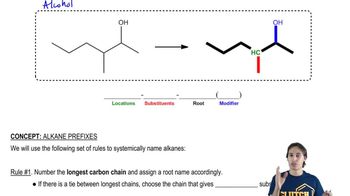


 1:11m
1:11mMaster How to find the root name for cycloalkanes with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning