Identify the functional groups in each of the following molecules. [The number of functional groups has been given to assist you.]
(c) [Three]
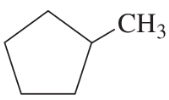
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: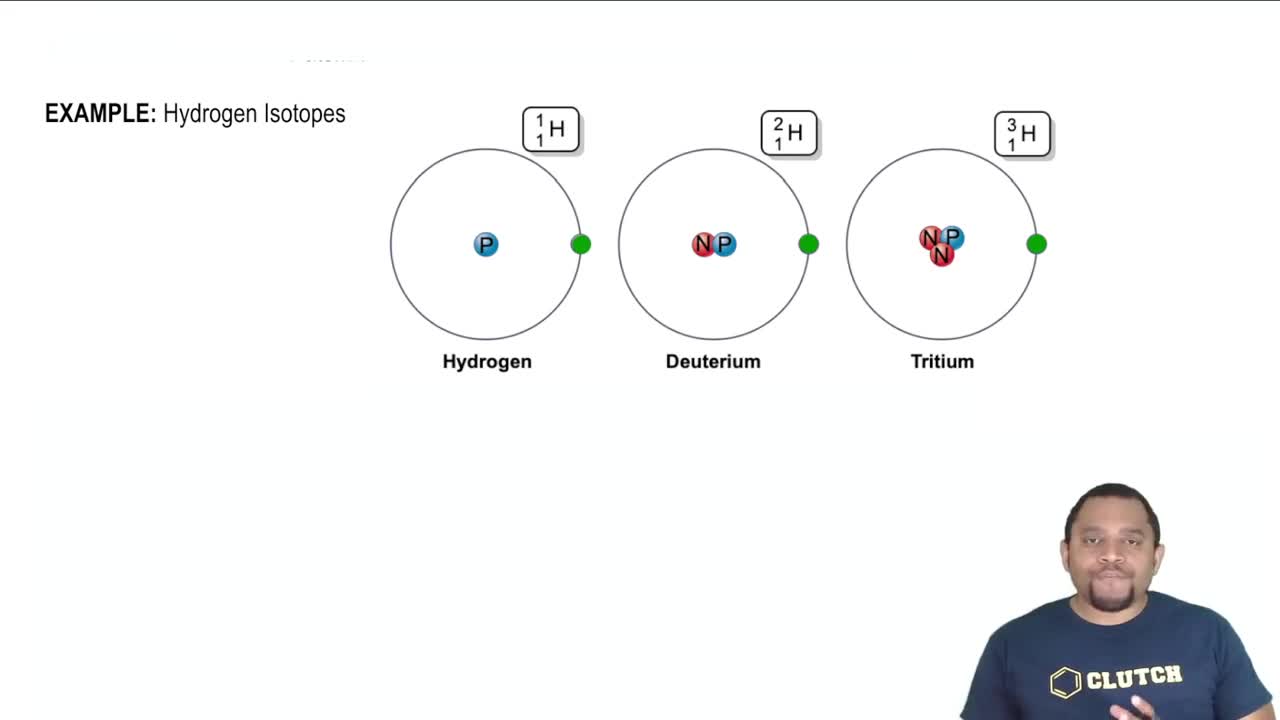
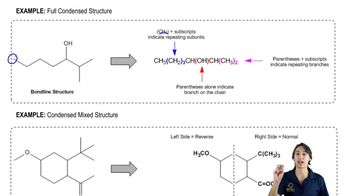

 1:49m
1:49mMaster Why we need functional groups. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning