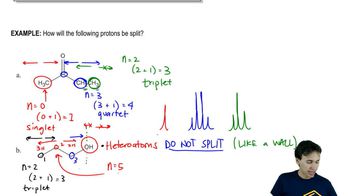
What products are formed when each of the following reacts with HO−?
a. CH3OH
b. +NH4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 2:49m
2:49mMaster The Lewis definition of acids and bases. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning