Consider the following reaction: HBr + -C≡N ⇌ Br− + HC≡N
a. What is the acid on the left side of the equation?
b. What is the base on the left side of the equation?
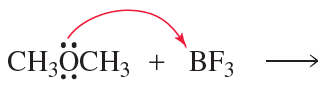
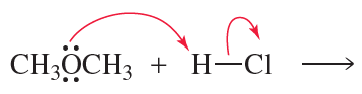
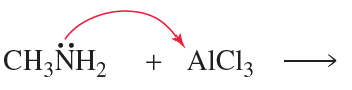
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 2:49m
2:49mMaster The Lewis definition of acids and bases. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning