The following compounds can all react as acids.
a. For each compound, show its conjugate base. Show any resonance forms if applicable. b. Rank the conjugate bases in the order you would predict, from most stable to least stable.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: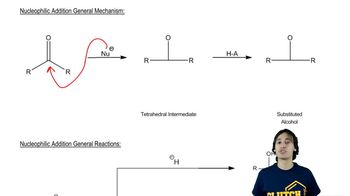
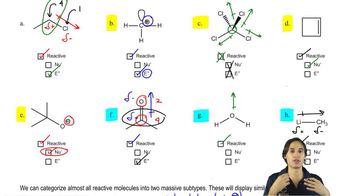


 2:49m
2:49mMaster The Lewis definition of acids and bases. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning