Refer to the following Lewis structures.
(c)
(d)
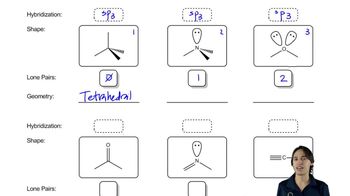
If an atom is sp² hybridized, how many sp²-hybridized orbitals does it use for bonding? How many p orbitals?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: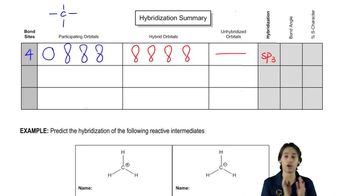


 2:53m
2:53mMaster How carbon creates 4 partially-filled orbitals. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning