Rank the following molecules by the length of the indicated bond from shortest to longest.
(a)
(b)
(c)
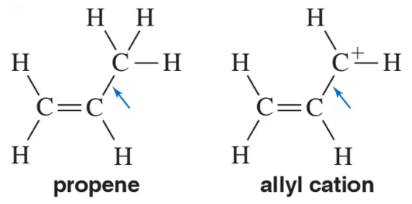
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance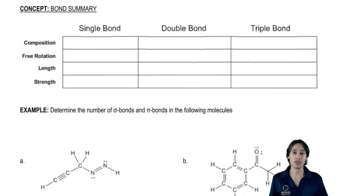
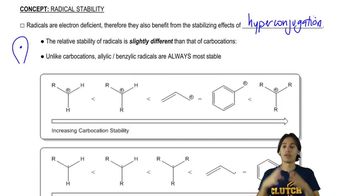
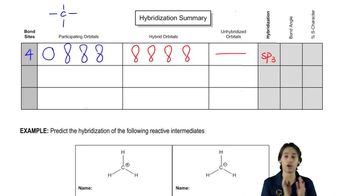

 6:00m
6:00mMaster Single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning