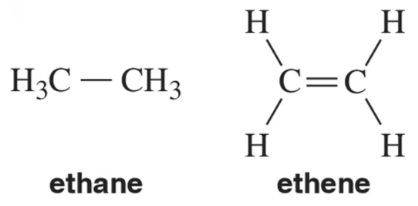
a. Which bond would be longer?
b. Which bond would be stronger?
3. H—Cl or H—F
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 6:00m
6:00mMaster Single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning