Draw a Fischer projection for each compound. Remember that the cross represents an asymmetric carbon atom, and the carbon chain should be along the vertical, with the IUPAC numbering from top to bottom.
(e)
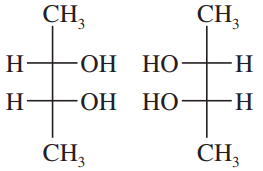
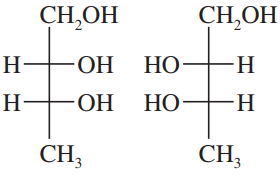
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 1:15m
1:15mMaster Introduction to different projections. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning