Draw the important resonance forms to show the delocalization of charges in the following ions. In each case, indicate the major resonance form(s).
(j)
(k)
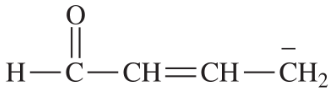
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: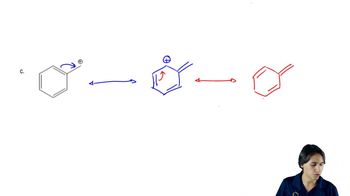


 3:34m
3:34mMaster The rules you need for resonance: with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning