Draw the important resonance forms of the following cations and anions:
(c)
(d)
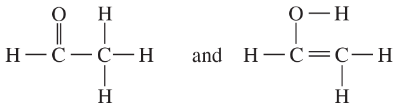
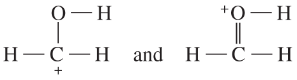
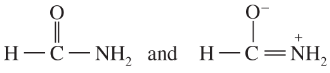
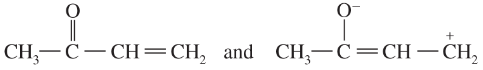
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
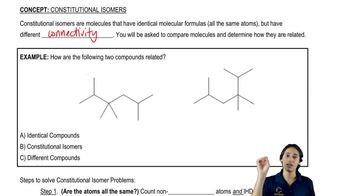
Verified video answer for a similar problem: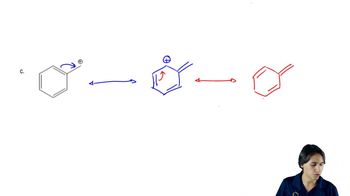

 3:34m
3:34mMaster The rules you need for resonance: with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning