Under certain conditions, the bromination of cyclohexene follows an unusual rate law:
b. What is the kinetic order with respect to bromine?
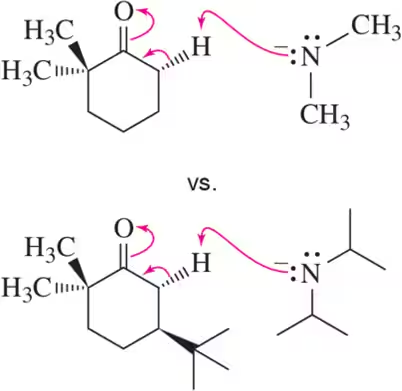
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 6:07m
6:07mMaster Introduction to free energy diagrams. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning