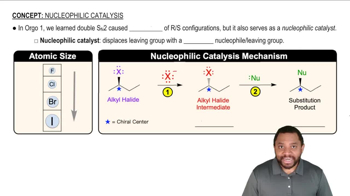
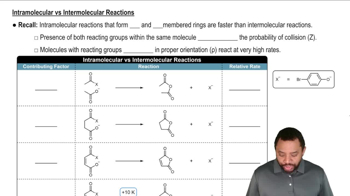
Within the following pairs, pick which reaction you would expect to be faster based on having a higher value of the frequency factor (A).
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: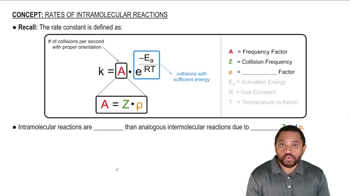

 6:07m
6:07mMaster Introduction to free energy diagrams. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning