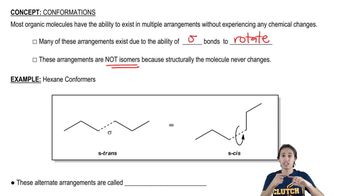
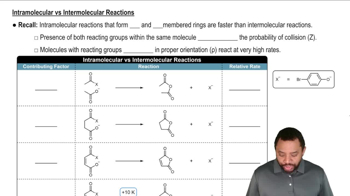
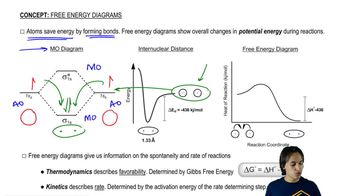
How will the rate of the reaction between bromomethane and hydroxide ion be affected if the following changes in concentration are made?
b. The concentration of the alkyl halide is cut in half and the concentration of the nucleophile is not changed.
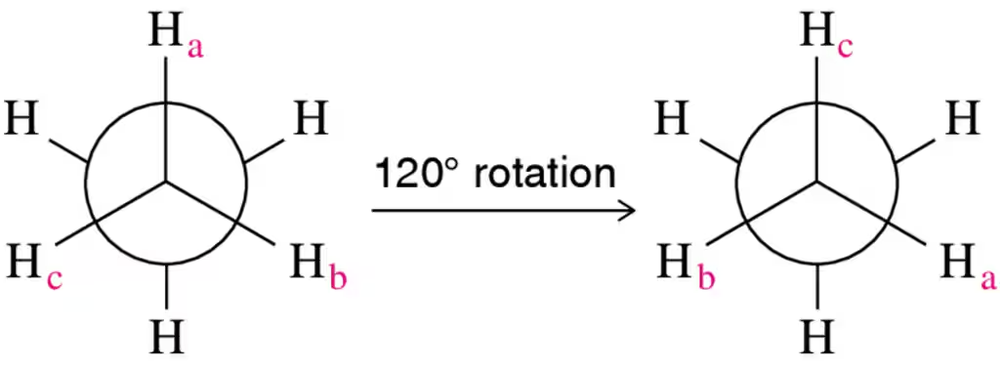
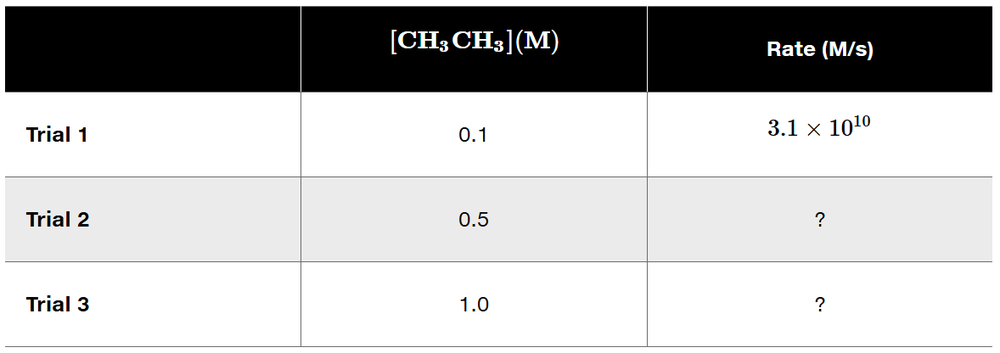
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: