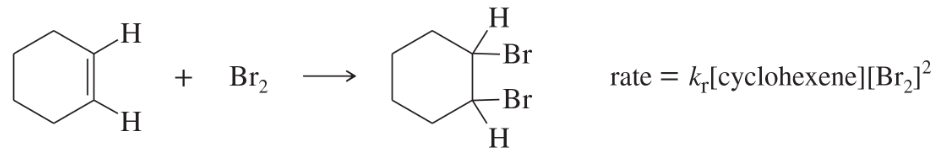
The reaction of tert-butyl chloride with methanol
is found to follow the rate equation
rate = kr[(CH3)3C—Cl]
c. What is the kinetic order overall
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:07m
6:07mMaster Introduction to free energy diagrams. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning