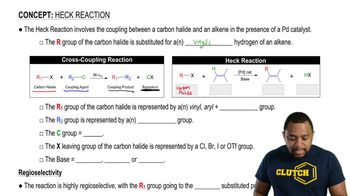
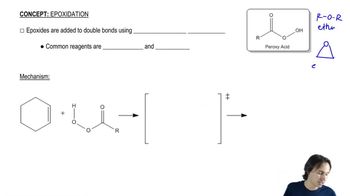
Retrosynthetic analysis is the process of working backward to develop the synthesis of a new compound. In Chapter 10, we begin developing multistep syntheses in this manner. For now, try to work backward a single step by suggesting an alkene and a reagent that would give products (a)–(i). [Your answers should not include alkenes that undergo rearrangement to give the desired products.]
(f)