Draw the product or products that will be obtained from the reaction of cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene with each of the following reagents. If a product can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
3. a peroxyacid
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: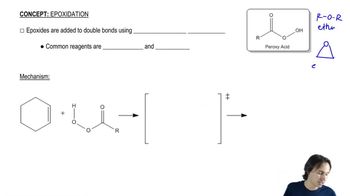



 2:19m
2:19mMaster General properties of epoxidation. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning