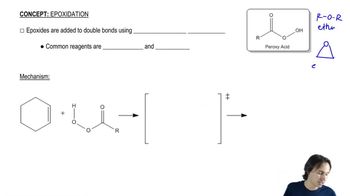
Predict the product(s) of each of the following reactions, making sure to indicate the relative stereochemical outcome. Indicate any racemic mixtures by drawing both enantiomers.
(a)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: