Reactions (a) and (b) are disfavored overall (∆G° > 0), yet they are favored based on ∆H°. Identify the bonds formed and broken for (a) and (b).
(b)
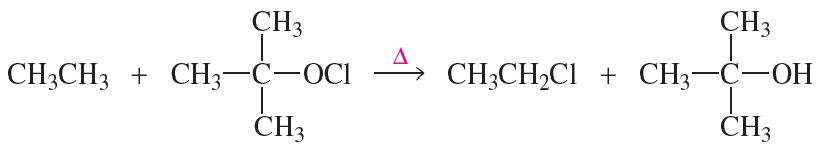
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 4:09m
4:09mMaster How to calculate enthalpy using bond dissociation energies. with a bite sized video explanation from Johnny
Start learning